¿Qué es un SaaS?
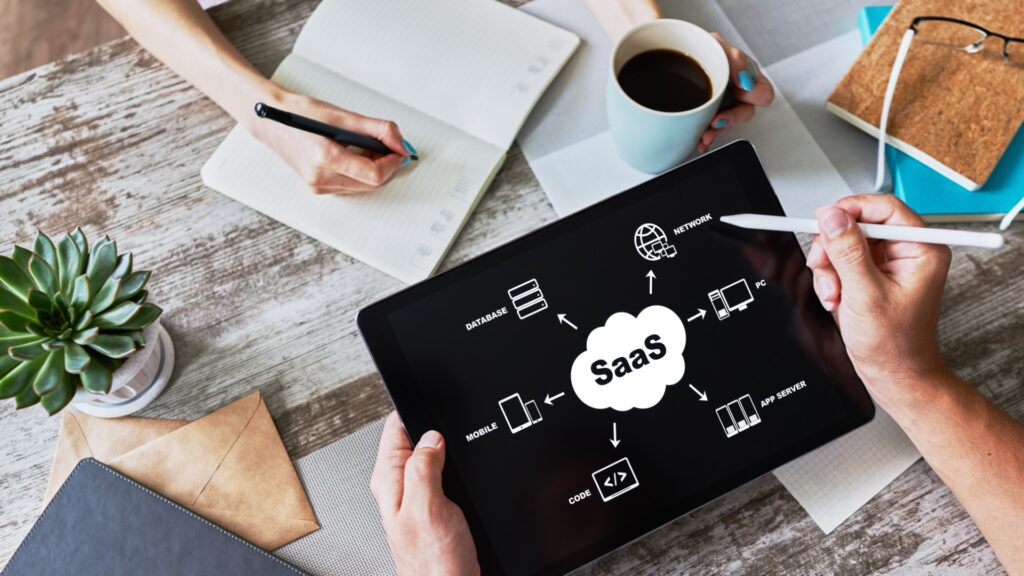

Si estás incursionando en el mundo digital, es probable que hayas oído hablar del término “SaaS”. Pero, ¿qué significa exactamente? El Software como Servicio, o SaaS, es un modelo de distribución de software que ha revolucionado la forma en que las empresas y los usuarios acceden y utilizan aplicaciones en línea. En este artículo, exploraremos en profundidad qué es un SaaS, cómo funciona y por qué es crucial para la eficiencia y la escalabilidad de las empresas modernas.
Importancia del SaaS
El Software como Servicio (SaaS) se ha convertido en un componente esencial en el entorno empresarial actual, ofreciendo una variedad de beneficios que transforman la forma en que las empresas operan. Profundicemos en la importancia del SaaS y su impacto en la gestión empresarial.
Accesibilidad a la Nube
Una de las características más destacadas del Software como Servicio (SaaS) es su accesibilidad a través de la nube. Esto significa que los usuarios pueden acceder a las aplicaciones y datos desde cualquier dispositivo con conexión a internet, sin importar su ubicación física. Profundicemos en la importancia de esta accesibilidad:
- Trabajo Remoto: Con el SaaS, los empleados pueden trabajar desde casa, en la oficina o en cualquier otro lugar donde tengan acceso a internet. Esto permite una mayor flexibilidad en los horarios de trabajo y mejora el equilibrio entre la vida laboral y personal.
- Colaboración en Tiempo Real: Las aplicaciones SaaS facilitan la colaboración entre equipos distribuidos geográficamente. Los usuarios pueden trabajar en documentos compartidos, hojas de cálculo y presentaciones en tiempo real, lo que mejora la productividad y la eficiencia del equipo.
- Disponibilidad Continua: Almacenar datos en la nube garantiza su disponibilidad continua, incluso en caso de fallos de hardware o problemas técnicos locales. Esto minimiza el tiempo de inactividad y asegura que los usuarios puedan acceder a sus aplicaciones y datos cuando los necesiten.
- Actualizaciones Automáticas: Las actualizaciones de software se implementan automáticamente en la nube, eliminando la necesidad de que los usuarios realicen actualizaciones manuales. Esto asegura que siempre tengan acceso a las últimas características y mejoras de seguridad sin interrumpir su flujo de trabajo.
Menos Costos Iniciales
Una de las ventajas más significativas del Software como Servicio (SaaS) es la reducción de los costos iniciales para las empresas. Profundicemos en la importancia de este aspecto:
- Eliminación de Costos de Infraestructura: Con el SaaS, las empresas no necesitan invertir en hardware costoso ni en la instalación y configuración de servidores locales. Esto significa que pueden comenzar a utilizar aplicaciones empresariales de forma rápida y sencilla, sin la necesidad de realizar una inversión inicial significativa en infraestructura tecnológica.
- Pago por Uso: En lugar de adquirir licencias de software tradicionales, que a menudo requieren un pago por adelantado considerable, el SaaS generalmente opera bajo un modelo de suscripción mensual o anual. Esto permite a las empresas pagar solo por los recursos que utilizan y escalar sus costos de acuerdo con sus necesidades y presupuesto.
- Reducción de Costos de Mantenimiento: Con el SaaS, los proveedores se encargan del mantenimiento continuo del software, incluidas las actualizaciones de seguridad y las mejoras de rendimiento. Esto elimina la necesidad de que las empresas contraten personal especializado o gasten recursos en el mantenimiento y la administración de sus sistemas informáticos.
Transforma tu ERP en un poderoso ecommerce B2B

Costos Continuos Reducidos
La naturaleza del Software como Servicio (SaaS) no solo reduce los costos iniciales, sino que también ofrece beneficios financieros a largo plazo para las empresas. Ahondemos en la importancia de la reducción de costos continuos:
- Modelo de Suscripción: El SaaS opera típicamente bajo un modelo de suscripción mensual o anual, lo que permite a las empresas pagar solo por los servicios que utilizan. Esta estructura de pago flexible elimina la necesidad de grandes inversiones de capital y proporciona a las empresas una mayor previsibilidad en sus gastos.
- Eliminación de Gastos de Mantenimiento: Los proveedores de SaaS se encargan del mantenimiento continuo del software, incluyendo actualizaciones de seguridad, parches y mejoras de rendimiento. Al externalizar estas tareas, las empresas reducen los costos asociados con el mantenimiento de infraestructura y la contratación de personal especializado.
Despliegue Rápido
Uno de los beneficios clave del Software como Servicio es su capacidad para ofrecer un despliegue rápido de aplicaciones empresariales. Veamos por qué este aspecto es tan importante:
- Implementación sin Problemas: Con el SaaS, las empresas pueden implementar nuevas aplicaciones en cuestión de días o incluso horas, en lugar de semanas o meses como suele ser el caso con el software tradicional. Esto significa que pueden poner en marcha soluciones empresariales de forma rápida y eficiente, sin las demoras asociadas con la instalación y configuración de servidores locales.
- Menor Tiempo de Inactividad: El despliegue rápido del SaaS minimiza el tiempo de inactividad y permite a las empresas comenzar a utilizar nuevas aplicaciones de inmediato. Esto es especialmente beneficioso en situaciones en las que se requiere una rápida adaptación a cambios en el mercado o en las operaciones comerciales.
- Pruebas y Personalización Ágiles: Las soluciones de SaaS suelen ofrecer opciones de personalización y configuración para adaptarse a las necesidades específicas de cada empresa. Esto permite a las empresas realizar pruebas y ajustes rápidos antes de implementar completamente una solución, lo que reduce el riesgo y acelera el proceso de adopción.
- Escalabilidad Instantánea: A medida que las empresas crecen, pueden escalar fácilmente sus suscripciones de SaaS para satisfacer la demanda adicional. Esto significa que no tienen que esperar a adquirir y configurar nuevos servidores o licencias de software, lo que acelera el proceso de expansión y permite a las empresas aprovechar oportunidades de crecimiento de manera más rápida y efectiva.
Escalabilidad Bajo Demanda
El concepto de escalabilidad bajo demanda es una de las características más poderosas del Software como Servicio (SaaS).
- Adaptación a las Necesidades del Negocio: Con el SaaS, las empresas pueden escalar sus recursos de manera rápida y eficiente para adaptarse a cambios en la demanda del mercado o en las operaciones internas. Esto significa que pueden aumentar o disminuir la capacidad de suscripción, el almacenamiento de datos o el número de usuarios según sea necesario, sin enfrentar las restricciones de hardware o licencias tradicionales.
- Flexibilidad para Crecer: La escalabilidad bajo demanda del SaaS permite a las empresas crecer de manera orgánica y sin limitaciones. A medida que aumenta el volumen de transacciones, el tráfico del sitio web o la cantidad de usuarios, las empresas pueden expandir sus recursos de forma inmediata y sin interrupciones en el servicio.
- Optimización de Costos: La capacidad de escalar recursos según la demanda permite a las empresas optimizar sus costos operativos. Pueden evitar gastos innecesarios al ajustar sus suscripciones de SaaS para satisfacer exactamente sus necesidades en cada momento, evitando así el desperdicio de recursos.
- Facilita la Innovación: La escalabilidad bajo demanda libera a las empresas de las limitaciones tecnológicas tradicionales, permitiéndoles experimentar y probar nuevas ideas con mayor libertad. Esto fomenta la innovación y la creatividad, ya que las empresas pueden adaptarse rápidamente a las oportunidades emergentes y las necesidades cambiantes del mercado.
Integra tu ERP con un ecommerce B2B con Stoam SaaS

Fiabilidad
La fiabilidad es un pilar fundamental ya que las empresas dependen de que las aplicaciones y servicios estén disponibles en todo momento. Aquí exploramos por qué la fiabilidad es tan esencial en el contexto del SaaS:
- Disponibilidad Continua: Los proveedores de SaaS se comprometen a ofrecer una disponibilidad del servicio alta, lo que significa que las aplicaciones están disponibles para los usuarios durante la mayor parte del tiempo. Este alto nivel de disponibilidad garantiza que las empresas puedan acceder a sus herramientas y datos críticos en cualquier momento, sin interrupciones en el servicio.
- Respaldo de Infraestructura Robusta: Los proveedores de SaaS invierten en infraestructura de servidor de alta calidad, centros de datos seguros y sistemas de respaldo redundantes para garantizar la fiabilidad del servicio. Esto minimiza el riesgo de tiempo de inactividad debido a fallas de hardware, errores de software o desastres naturales.
- Actualizaciones y Mantenimiento Transparentes: Los proveedores de SaaS realizan actualizaciones de software y mantenimiento de infraestructura de forma regular, pero planificada y transparente. Estas actualizaciones se realizan típicamente fuera del horario laboral o en momentos de menor actividad para minimizar el impacto en los usuarios finales.
- Soporte Técnico Especializado: Los proveedores de SaaS suelen ofrecer servicios de soporte técnico dedicados para ayudar a los clientes a resolver problemas y responder preguntas relacionadas con el uso del software. Esto garantiza que las empresas puedan obtener ayuda rápidamente en caso de problemas técnicos o dificultades de uso.
- Cumplimiento de Acuerdos de Nivel de Servicio (SLA): Los proveedores de SaaS suelen establecer Acuerdos de Nivel de Servicio (SLA) que especifican la calidad del servicio que se debe proporcionar, incluyendo la disponibilidad del servicio, los tiempos de respuesta y otros parámetros clave. Esto proporciona a las empresas una garantía adicional de fiabilidad y rendimiento del servicio.
Integración
La integración es un aspecto clave del SaaS, ya que permite a las empresas aprovechar al máximo sus aplicaciones al conectarlas de manera fluida y eficiente. Aquí exploramos la importancia de la integración en el contexto del SaaS:
- Flujo de Trabajo Unificado: La integración del SaaS permite a las empresas crear un flujo de trabajo unificado al conectar diferentes herramientas y aplicaciones. Esto significa que los datos pueden fluir sin problemas entre sistemas, eliminando la necesidad de realizar tareas manualmente y reduciendo el riesgo de errores humanos.
- Mejora de la Productividad: Al integrar aplicaciones de SaaS con otras herramientas utilizadas en la empresa, los empleados pueden acceder y compartir datos de manera más rápida y eficiente. Esto mejora la productividad al reducir el tiempo dedicado a la búsqueda de información y la transferencia manual de datos entre sistemas.
- Mayor Visibilidad y Control: La integración del SaaS proporciona a las empresas una vista completa y centralizada de sus datos al conectar diferentes sistemas y fuentes de información. Esto permite una mejor toma de decisiones al proporcionar información más precisa y actualizada en tiempo real.
- Personalización y Escalabilidad: Las empresas pueden personalizar la integración del SaaS para satisfacer sus necesidades específicas y adaptarse a medida que crecen y evolucionan. Esto significa que pueden agregar nuevas integraciones según sea necesario y escalar sus sistemas de manera flexible para satisfacer las demandas cambiantes del negocio.
- Acceso a Ecosistemas de Aplicaciones: Muchos proveedores de SaaS ofrecen APIs (interfaces de programación de aplicaciones) que permiten a las empresas integrar sus aplicaciones con otros sistemas externos y servicios en la nube. Esto les brinda acceso a un amplio ecosistema de aplicaciones y servicios que pueden enriquecer y ampliar las capacidades de sus sistemas existentes.
Datos y Análisis en Tiempo Real
La capacidad de acceder a datos y análisis en tiempo real es un componente crucial del Software como Servicio (SaaS), ya que permite a las empresas tomar decisiones informadas y ágiles. Aquí exploramos la importancia de esta funcionalidad en el contexto del SaaS:
- Información Accesible al Instante: Con el SaaS, las empresas pueden acceder a datos actualizados al instante, lo que les permite monitorear y comprender mejor el rendimiento de sus operaciones en tiempo real. Esto significa que los equipos pueden tomar decisiones fundamentadas sobre la marcha, sin tener que esperar a que se generen informes o se recopilen datos manualmente.
- Identificación de Tendencias y Patrones: La capacidad de analizar datos en tiempo real permite a las empresas identificar tendencias emergentes y patrones de comportamiento de manera rápida y eficiente. Esto les brinda la oportunidad de anticipar cambios en el mercado, ajustar estrategias comerciales y capitalizar oportunidades de manera proactiva.
- Optimización de Procesos: Los datos en tiempo real permiten a las empresas optimizar sus procesos operativos al identificar cuellos de botella, ineficiencias y áreas de mejora de manera inmediata. Esto les permite realizar ajustes en tiempo real para aumentar la eficiencia y reducir los costos operativos.
- Mejora de la Experiencia del Cliente: Al tener acceso a datos en tiempo real sobre el comportamiento y las preferencias de los clientes, las empresas pueden personalizar la experiencia del cliente de manera más efectiva. Esto les permite ofrecer productos y servicios adaptados a las necesidades individuales de cada cliente, lo que mejora la satisfacción y fidelización del cliente.
- Análisis Predictivo: La capacidad de analizar datos en tiempo real también permite a las empresas utilizar técnicas de análisis predictivo para prever tendencias futuras y tomar medidas preventivas. Esto les ayuda a mitigar riesgos, identificar oportunidades de crecimiento y mantenerse un paso adelante de la competencia.

Comparación con otros modelos de servicios en la nube
Para comprender mejor el Software como Servicio (SaaS), es fundamental contextualizarlo dentro del panorama más amplio de los servicios en la nube. A continuación, analizaremos cómo se compara el SaaS con otros modelos de servicios en la nube, como la Plataforma como Servicio (PaaS) y la Infraestructura como Servicio (IaaS)
SaaS vs. Plataforma como Servicio (PaaS)
Al comparar el Software como Servicio (SaaS) con la Plataforma como Servicio (PaaS), es importante entender las diferencias fundamentales entre estos dos modelos de servicios en la nube. A continuación, analizaremos cómo difieren el SaaS y PaaS en términos de funcionalidad, flexibilidad y uso:
- Entrega de Software vs. Entorno de Desarrollo: La principal diferencia entre SaaS y PaaS radica en su enfoque principal. Mientras que el SaaS se centra en la entrega de aplicaciones listas para usar a través de internet, PaaS proporciona a los desarrolladores un entorno de desarrollo en la nube para crear, personalizar y alojar aplicaciones.
- Listo para Usar vs. Personalizable: Con el SaaS, los usuarios tienen acceso inmediato a aplicaciones completamente desarrolladas y listas para usar, sin necesidad de realizar ninguna configuración adicional. En contraste, PaaS ofrece a los desarrolladores una plataforma y herramientas para construir y personalizar aplicaciones según sus necesidades específicas.
- Gestión de la Infraestructura: En el caso del SaaS, la gestión de la infraestructura subyacente es responsabilidad del proveedor del servicio en la nube. Los usuarios solo necesitan preocuparse por el uso y la configuración de la aplicación en sí. Por otro lado, con PaaS, los desarrolladores tienen más control sobre el entorno de desarrollo, pero también asumen más responsabilidad en términos de gestión de la infraestructura y la seguridad.
- Flexibilidad y Control: Si bien el SaaS ofrece conveniencia y simplicidad al proporcionar aplicaciones listas para usar, PaaS ofrece a los desarrolladores más flexibilidad y control sobre el proceso de desarrollo y despliegue de aplicaciones. Esto permite a los desarrolladores personalizar completamente el software y adaptarlo a las necesidades específicas de su empresa.
- Casos de Uso: El SaaS es ideal para empresas que buscan soluciones de software rápidas y listas para usar, como herramientas de productividad, gestión de relaciones con el cliente (CRM) o recursos humanos. Por otro lado, PaaS es más adecuado para empresas que desean crear aplicaciones personalizadas o desarrollar software específico para sus necesidades comerciales únicas.
SaaS vs. Infraestructura como Servicio (IaaS)
- Entrega de Software vs. Acceso a Infraestructura: La principal diferencia entre SaaS e IaaS radica en su enfoque fundamental. Mientras que el SaaS se centra en la entrega de aplicaciones listas para usar a través de internet, IaaS proporciona a las empresas acceso a recursos de infraestructura en la nube, como servidores virtuales, almacenamiento y redes.
- Gestión de la Infraestructura: Con el SaaS, la gestión de la infraestructura subyacente es responsabilidad del proveedor del servicio en la nube. Los usuarios solo necesitan preocuparse por el uso y la configuración de la aplicación en sí. Por otro lado, con IaaS, los usuarios tienen más control sobre la infraestructura subyacente y son responsables de administrar y mantener los recursos de la nube.
- Listo para Usar vs. Personalización: El SaaS ofrece a los usuarios acceso inmediato a aplicaciones completamente desarrolladas y listas para usar, sin necesidad de realizar ninguna configuración adicional. En contraste, IaaS proporciona a las empresas una infraestructura básica en la nube que puede ser personalizada y configurada según sus necesidades específicas.
- Flexibilidad y Control: Si bien el SaaS ofrece conveniencia y simplicidad al proporcionar aplicaciones listas para usar, IaaS ofrece a las empresas más flexibilidad y control sobre su infraestructura de TI. Esto permite a las empresas personalizar y escalar recursos según sea necesario para satisfacer las demandas cambiantes del negocio.
- Casos de Uso: El SaaS es ideal para empresas que buscan soluciones de software rápidas y listas para usar, como herramientas de productividad, gestión de relaciones con el cliente (CRM) o recursos humanos. Por otro lado, IaaS es más adecuado para empresas que desean construir y administrar su propia infraestructura de TI en la nube, utilizando recursos como servidores virtuales, almacenamiento y redes según sea necesario.
Elección de la estrategia adecuada para empresas B2B
En el entorno empresarial B2B, elegir la estrategia adecuada entre omnicanalidad y multicanalidad es crucial para alcanzar los objetivos de comunicación y satisfacción del cliente. A continuación, se presentan los factores a considerar en esta decisión.
Factores a considerar en la decisión
- Objetivos comerciales
- Recursos disponibles
- Segmentación de clientes
- Competencia en el mercado
Si bien la elección entre omnicanalidad y multicanalidad es importante, existe otra alternativa. También es válido considerar la posibilidad de combinar ambas estrategias de manera sinérgica.
Integrar elementos de ambas puede ofrecer una mayor cobertura de mercado y una experiencia de cliente más enriquecedora que se adapte mejor a tus necesidades.
La larga experiencia de Stoam trabajando con empresas B2B nos permite ofrecer soluciones para todo tipo de proyectos. Estamos dispuestos a desarrollar una solución estandarizada y adaptada a tus necesidades. ¡Contacto hoy mismo y juntos llevemos a tu empresa al éxito!
Compartir:
Related Articles

What is a marketplace? Find out how to get the most out of it
What is a marketplace? Find out how to get the most out of it In today’s digital world, marketplaces have

Business to consumer (B2C): how it works and how it differs from B2B
Business to consumer (B2C): how it works and how it differs from B2B In today’s world, e-commerce and direct business-to-consumer

Alibaba revolutionises B2B commerce with ‘Accio’ – the AI-powered search engine for SMEs
Alibaba revolutionises B2B commerce with ‘Accio’ – the AI-powered search engine for SMEs Share: Tabla de contenidos What is Accio

Examples of market segmentation: How to apply it in different sectors?
Examples of market segmentation: How to apply it in different sectors? In today’s competitive business landscape, market segmentation is more

Omni-channel strategy: How to integrate all channels to improve customer experience
Omni-channel strategy: How to integrate all channels to improve customer experience In a world where consumers use multiple channels to

What are open APIs and their role in SaaS solutions?
What are open APIs and their role in SaaS solutions? Open APIs have transformed the way businesses use software, especially

Analysis of B2B marketplaces: Are they an opportunity or a threat?
Analysis of B2B marketplaces: Are they an opportunity or a threat? B2B marketplaces are transforming the way companies buy and

How to use chatbots in B2B ecommerce to improve conversions
How to use chatbots in B2B ecommerce to improve conversions In the world of ecommerce B2B (Business to Business)shopper expectations

ERP and sustainability: How a system can reduce environmental impact
ERP and sustainability: How a system can reduce environmental impact Sustainability has become a crucial priority in today’s business landscape.
Automatiza los pedidos con el ecommerce b2b de Stoam SaaS

